Are you working in your business or working on your business?
When reviewing your business, whether as a manager or as a business owner, it is sometimes overwhelming as you try to decide what information is important and why. You may use your business review to decide the direction of the business for the next 12 months or even as part of a three or five year plan. Read on to discover the tools and models which could help you.
Porter’s 5 Forces model
The ability for you to make good profits in your business is dependent upon the strength of your position in the market.
This is where a tool like Porter’s 5 Forces is useful as it helps you discover who has the most power in a given situation.
This tool was created by Harvard Business School professor Michael Porter and published in 1979. It is still useful and relevant today. Porter encouraged looking beyond just competitors when considering your business. It can also show you if a new/existing product or service is likely to be profitable for you.
The tool assumes that there are five forces that determine competitive power in a business situation.
Any of them can work for or against you, so it’s important to understand them.
Porter's 5 forces:
- Threat of substitute products or services.
- Threat of established rivals.
- Threat of new entrants to your market.
- Bargaining power of your suppliers.
- Bargaining power of your customers.
By completing a 5 Forces analysis, you’ll be able to see where you’re at risk and plan to overcome this.
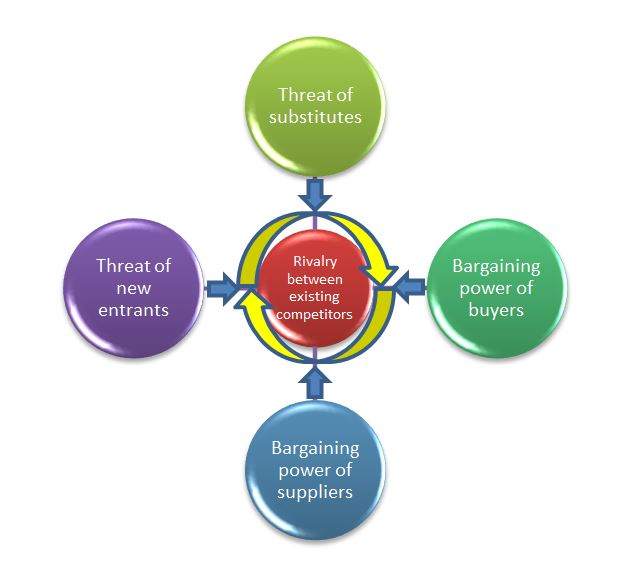
To use Porter’s Five Forces as an analysis tool, you need to look at each one individually.
1) Rivalry between existing competitors
This looks at the number and strength of your competitors.
- How many competitors do you have?
- Are their products or services as good as or even better than yours?
- How can you establish a strong advantage over them?
When competitive rivalry is low, a company has greater power to do what it wants to do to achieve higher sales and profits.
When competitive rivalry is high, competitors can try to attract customers with aggressive price cuts and high-impact marketing campaigns. In markets with lots of rivals, your suppliers and buyers can go elsewhere if they feel that they’re not getting a good deal from you.
2) Bargaining power of suppliers
This force examines how easily suppliers can drive up the price of goods or services.
It is affected by the number of suppliers and the basics of supply and demand.
The fewer the number of suppliers, and the more a company depends upon a supplier, the more power a supplier holds. This can impact your profits substantially.
If you have several suppliers of a particular product or service to choose from, you can switch to a cheaper alternative if prices are too high. The more you have to choose from, the easier it will be to switch to a cheaper alternative.
3) Bargaining power of buyers.
This examines the ability customers have to drive prices down.
It is affected by how many customers a business has, how significant each customer is to that business, and how much it would cost a customer to switch from one company to another.
The smaller and more powerful a client base, the more power it holds. Are your customers strong enough to dictate terms to you? If you deal with only a few customers, they have more power, but your power increases if you have many customers.
4) Threat of substitutes
How easy is it for your customers to find another way to get what you’re offering?
A substitution that is easy and cheap to make can weaken your position and threaten your profitability. The easier it is, the more your business’ power is weakened.
An example of this may be purchasing contact lenses and solutions online.
5) Threat of new entrants
Identify how easy/likely it is for new competitors to enter the market. The easier it is for them to swoop in, the harder it is for you to make a profit.
- How easy is it to get a foothold in your industry or market?
- How much would it cost?
- How tightly is your sector regulated?
If you are in an industry with strong barriers to entry, this would be attractive for companies that would prefer to operate in a space with fewer competitors.
Using the Porter’s 5 Forces model
- Gather the information on each of the five forces.
Business owners/ managers should gather information about their industry and check it against each of the factors influencing the 5 forces.
- Analyse the results and display them on a diagram.
After gathering all the information, you should analyse it and determine how each force is affecting your business and industry.
- Formulate strategies based on the conclusions.
Business owners/managers should formulate business’ strategies using the results of the analysis.
Porter’s 5 forces is a great tool but has its limitations and requires further analysis to be done, such as SWOT or PESTLE.
Useful web links:
https://www.isc.hbs.edu/strategy/business-strategy/Pages/the-five-forces.aspx
https://hbr.org/1979/03/how-competitive-forces-shape-strategy
Download here

