Retina
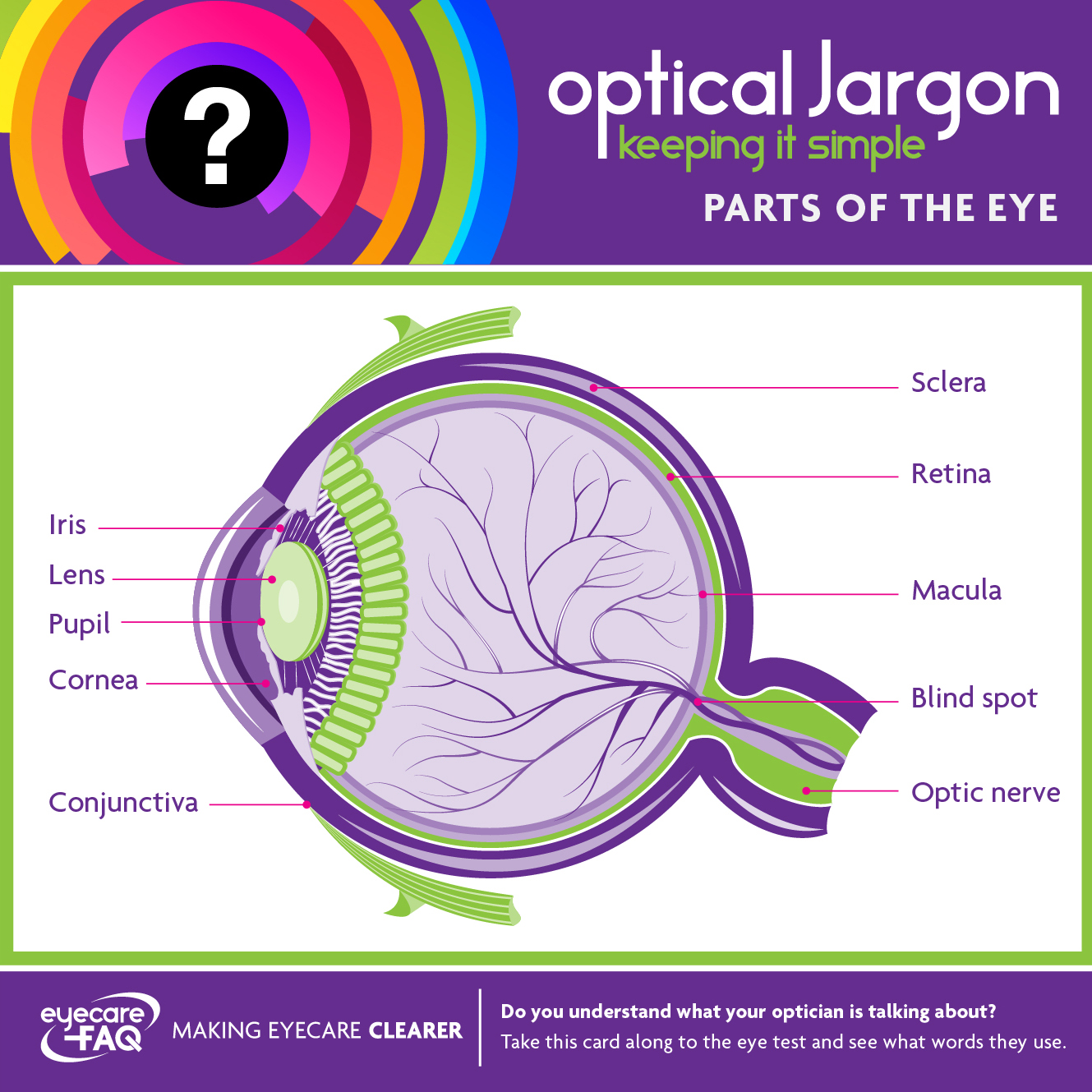
The retina is the layer of cells and nerve fibres at the back of the eye. The cells detect light and the nerve fibres send messages to the brain allowing you to see.
Blind spot
The blind spot is the part of the retina at the back of the eye where all the nerves come together to form the optic nerve head and exit the eye on the way to the brain. As it sounds, there is no vision in this area, but each eye compensates for the other eye’s blind spot so you don’t notice.
Cone
A cone is a retinal nerve cell at the back of your eye. Cones help you see in fine detail and perceive colour. They are most concentrated at the centre of your retina, the macula.
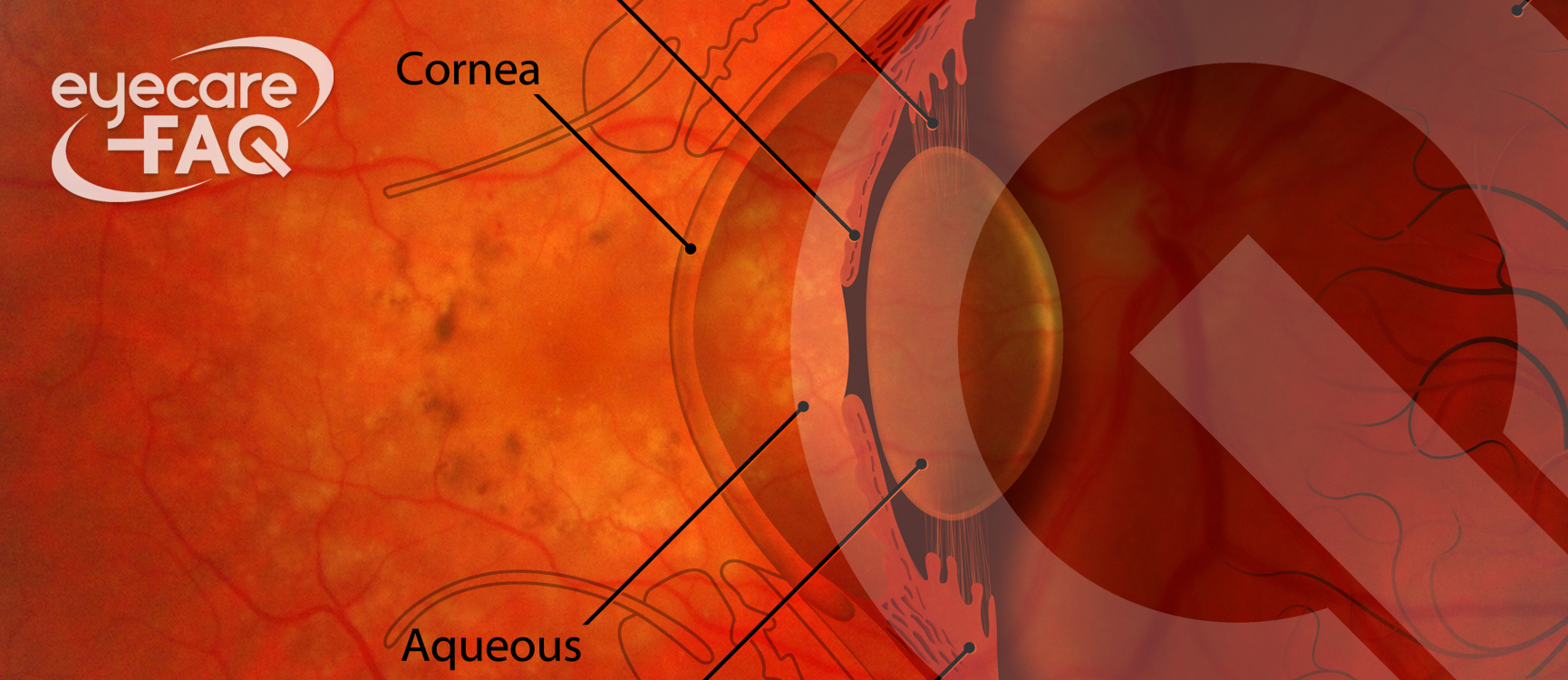
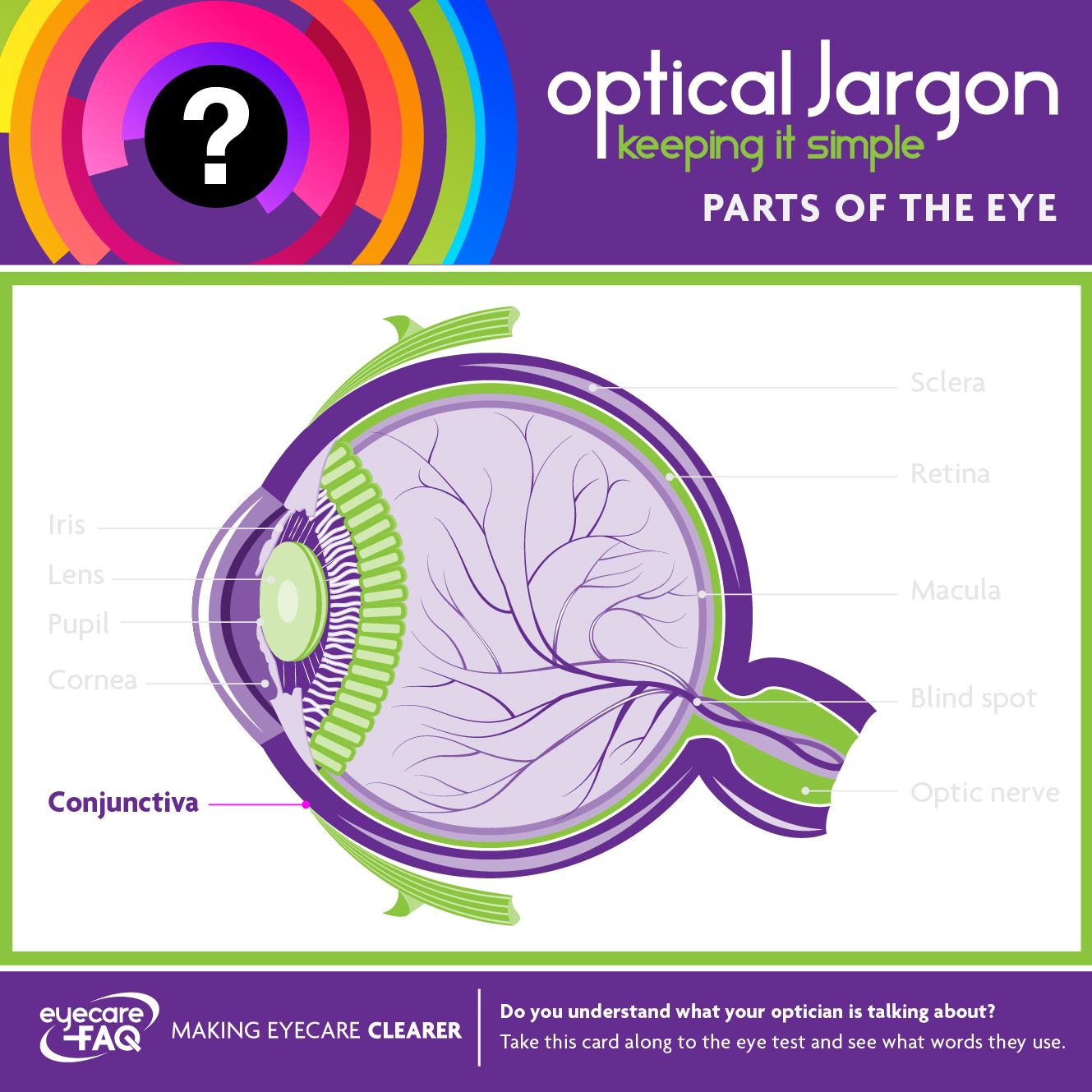
Conjunctiva
The conjunctiva is a thin transparent membrane that covers the front of the eye and lines the inside of the eyelids. It helps lubricate the eye by producing mucus and a small amount of tears.
Cornea
The cornea is the transparent layer at the front of the eye that covers the iris and pupil. It is curved, which helps light to focus on the back of your eye for clear vision.
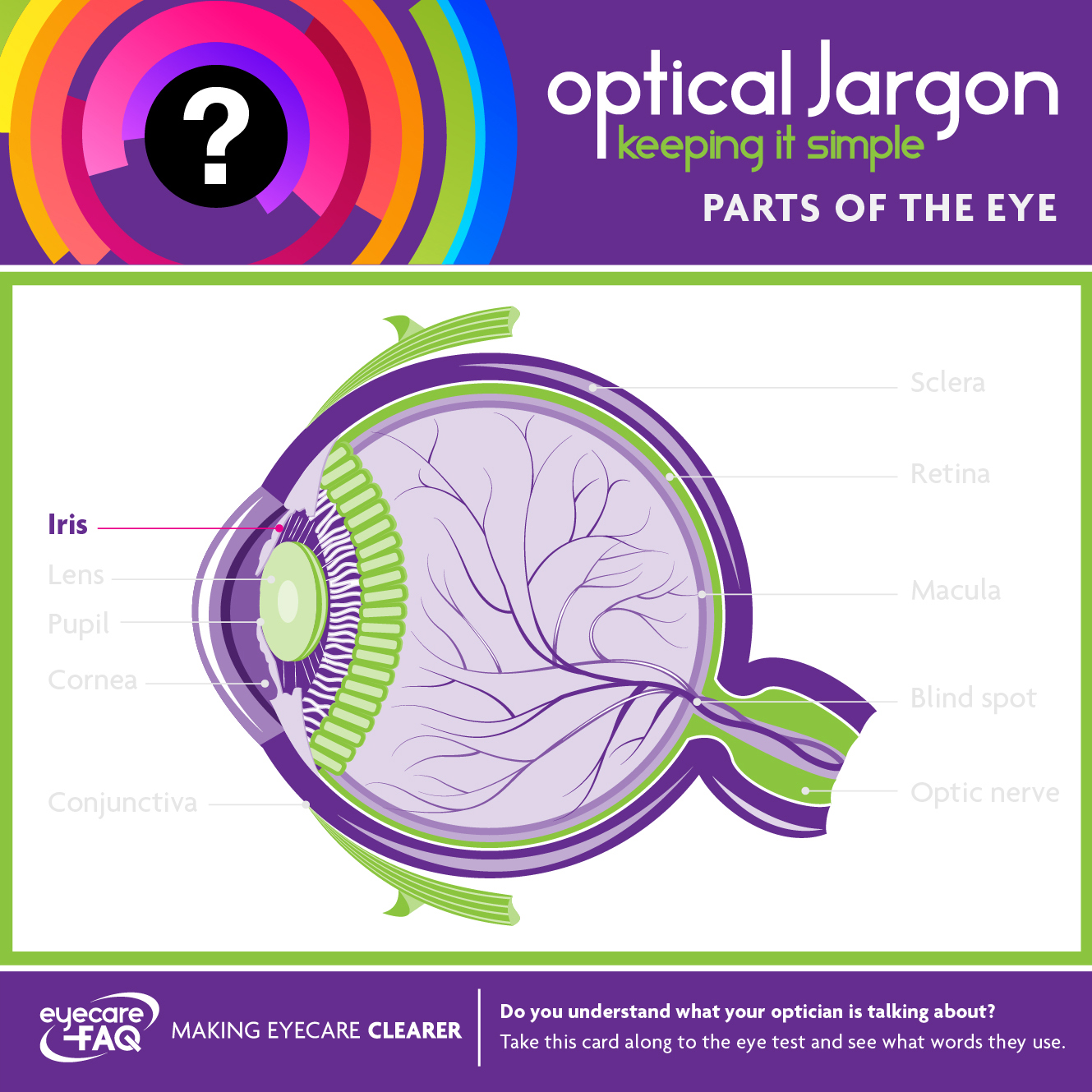
Iris
The iris is the coloured part of the eye. It dilates and constricts to allow more or less light into the eye, according to the light levels that surround you.
Lens
The lens is a clear transparent structure that is held inside your eye by the lens capsule. It is designed to be flexible, to allow you to focus on near objects. The lens becomes less flexible over time, which is why many people need reading glasses. Eventually the lens becomes cloudy: this is called cataract.
Macula
The macula is a tiny area at the centre of the retina which is made up of densely packed cone cells. This gives you the best fine detail vision.
Optic nerve
The optic nerve is a bundle of nerve fibres that carry information from the retina to the brain.
Pupil
The pupil is the name for the hole in the centre of the iris. It increases in size in low light conditions to allow you to see more, and protects the eye by decreasing in size in bright light.
Rod
A rod is a cell that forms part of the retina, the nerve cell layer at the back of your eye. Rods help you see in low light levels and in general detail. There are not involved in colour vision, and form the majority of cells at the back of the eye.
Sclera
The sclera is the white part of the eye that you can see surrounding the coloured iris. In fact, it encloses and protects the whole eyeball. It is opaque – it doesn’t let light in – and is made up of collagen and elastin.