Are you working in your business or working on your business?
When reviewing your business, whether as a manager or as a business owner, it is sometimes overwhelming as you try to decide what information is important and why. You may use your business review to decide the direction of the business for the next 12 months or even as part of a three or five year plan. Read on to discover the tools and models which could help you.
Balanced Scorecard
Rather than falling into the habit of focussing on short-term actions, the Balanced Scorecard helps a business to consider the longer term.
This model looks at an organisation’s financial resources available, the customer view of performance, the quality and efficiency of internal processes and the ability of the organisation to achieve its targets.
The balanced scorecard was first introduced by accounting academic Dr Robert Kaplan and business executive and theorist Dr David Norton. It was first published in 1992 in the Harvard Business Review.
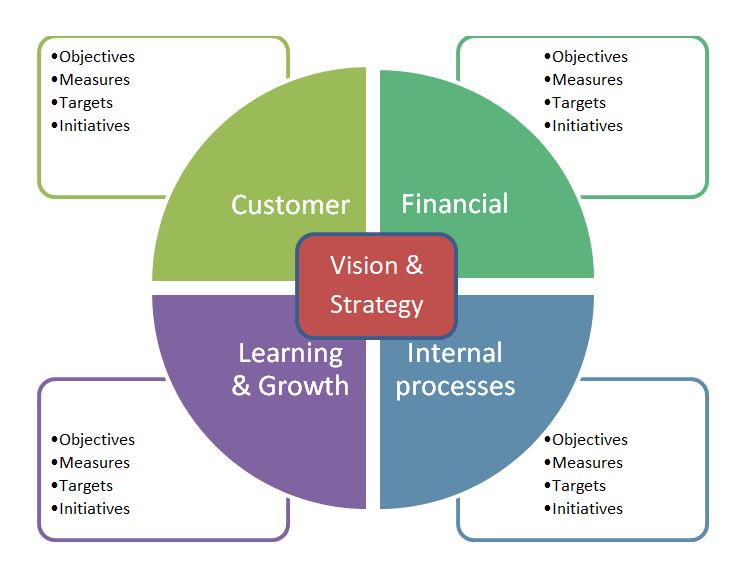
A balanced scorecard is a performance metric used in strategic management to identify and improve a business’s various functions and their resulting outcomes. It involves measuring four main aspects of a business: learning and growth, internal processes, customers, and finance.
Learning and growth
These are analysed through the investigation of training and knowledge resources. This first area looks at how well information is captured and how effectively employees utilise the information to convert it to a competitive advantage in the sector.
Internal processes
These are evaluated by investigating how well products are manufactured. Operational management is analysed to track efficiency, gaps, delays, bottlenecks, shortages, or waste.
Customer perspectives
These are collected to gauge customer satisfaction with service levels, quality, price, and availability of products or services. Customers provide feedback about their satisfaction with current products and services. The existence of alternatives (those of the competitor) has a large influence on customer expectation.
Financial data
Areas such as sales, expenditures, and income are used to understand financial performance. These financial metrics may include £ amounts, financial ratios, budget variances, or income targets.
The implementation of the Balanced Scorecard can be carried out in different ways which could include the following steps:
- Set up a vision, mission and strategic objectives for the business.
- Perform an analysis to gauge the expectations of customers.
- Make a list of the critical success factors.
- Translate strategic objectives into goals.
- Set up key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the objectives.
- Translate the objectives into operational activities.
- Involve teams/employees to achieve buy-in and ownership.
Useful web links:
balancedscorecards.com/balanced-scorecard/#learn-perspectives
hbr.org/1992/01/the-balanced-scorecard-measures-that-drive-performance-2
www.toolshero.com/strategy/balanced-scorecard/

